The Best Google Search Console Filter To Measure AI Overview Performance
The search landscape has shifted. With the rise of Google’s AI Overviews, a massive chunk of organic traffic is being intercepted by large language models (LLMs) that provide direct answers right on the SERP.
The problem for SEOs is the “Data Blind Spot.” Currently, Google Search Console (GSC) lumps AI Overview impressions in with standard organic results. There is no native “AI Traffic” button or web filter to measure AI vs. Maps vs. regular SEO rankings. This makes it nearly impossible to distinguish traditional keyword searches from the conversational queries that trigger AI answers.
Until Google releases official data, we need a reliable proxy. Furthermore, API data only goes back 16 months! We are a year into AI Overviews crushing search, so it’s now or never time.
Enter our “AI Super Filter.” By applying a specific Regular Expression (Regex) in GSC, you can isolate the types of queries Google’s AI is designed to answer. This allows you to measure your performance in the “AI-Vulnerable” segment of search.
Here is the filter, how to set it up, and how we use it to measure your true impact.
The Breakdown: The Components of AI Intent
To build the super filter, we need to understand the three main buckets of queries that trigger AI results. Even if this filter doesn’t capture every AI trigger, it does an excellent job of capturing the intent most likely to be served by one.
1. The Interrogators (Who, What, Where, When, Why, How)
This is the bread and butter of informational search. In the past, a user asking “how to fix a leaky faucet” might click three different articles. Today, an LLM reads those three articles and summarizes the steps. If a query starts with one of the “5 Ws” (or “How”), the user is looking for a definitive answer.
The Logic: We also include auxiliary verbs like “is,” “are,” and “can,” which often signal definitive Yes/No questions that AI loves to answer (e.g., “Can dogs eat grapes?”).
2. The Comparison Seekers (“Vs” / “Difference”)
Users searching for comparisons are asking Google to perform a synthesis task. They don’t want to read Review A and then Review B; they want to know how A compares to B instantly. Google’s AI often handles these by generating side-by-side comparison tables directly on the results page.
The Logic: Words like “versus,” “compare,” and “pros and cons” are strong signals of this intent.
3. The Evaluators (“Best” / “Top”)
These are high-value, mid-funnel commercial investigation queries. Someone searching for “best CRM for small business” is looking for recommendations. Previously, this was dominated by affiliate listicles. Now, AI Overviews aggressively target these queries, providing carousels of products or bulleted lists culled from top-ranking reviews.
Our Master-AI Regex Filter
Instead of running three separate reports, we combine these concepts into one powerful Regular Expression.
This filter casts a wide net, capturing queries that start with question words OR contain comparison/evaluation markers anywhere in the phrase. It uses the (?i) flag to ensure it is case-insensitive.
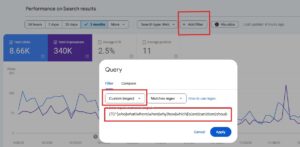
Copy this Regex Filter String:
(?i)^(who|what|where|when|why|how|which|is|are|can|does|should)|\b(vs|versus|compare|difference|pros and cons|guide|tutorial|best|top|list)\b
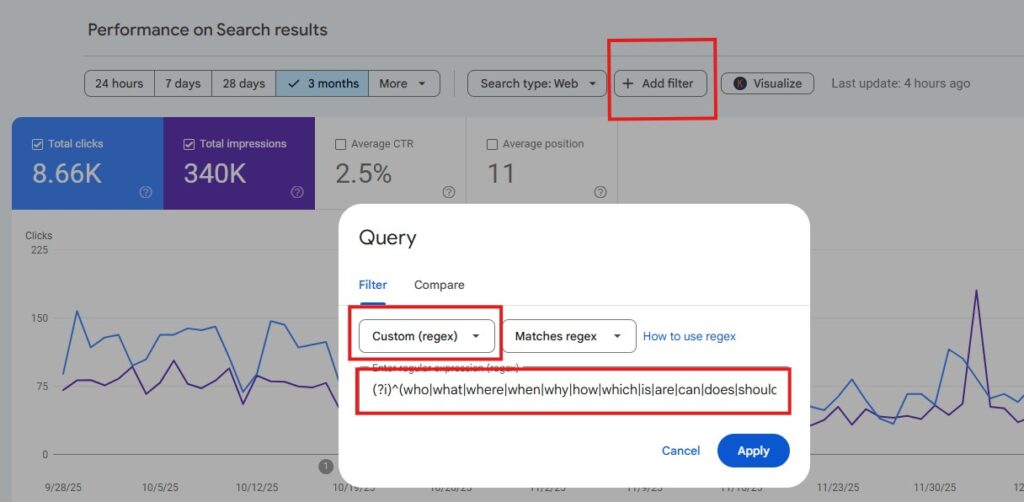
How to Add the “AI Super Regex” in Google Search Console
Follow these steps to apply this filter to your own property.
Open Google Search Console: Navigate to your property and click on Performance (or “Search results”) in the left-hand sidebar.
Locate the Filter Bar: Look at the top of the chart where you see filters for “Search type: Web,” “Date,” etc. Click the + New bubble.
Select Query: In the dropdown menu that appears, select Query…
Choose Custom Regex:
Click the dropdown that says “Queries containing” and change it to Custom (Regex).
Note: If you don’t see “Custom (Regex),” ensure you are in the “Query” filtering menu, not “Page” or “Country.”
Paste and Apply: Paste the regex string from the section above into the text field and click Apply.
Your performance chart will now reload to show only the traffic matching these high-intent, conversational queries.
Beyond the Query Tab: Analyzing Impact
The real power of this filter unlocks when you apply it and then navigate away from the “Queries” tab. Because GSC filters persist across different views, you can use this super filter to diagnose the AI-health of your site beyond queries.
The Landing Page Report
Once the AI-prompt regex filter is applied, click on the Pages tab below the chart.
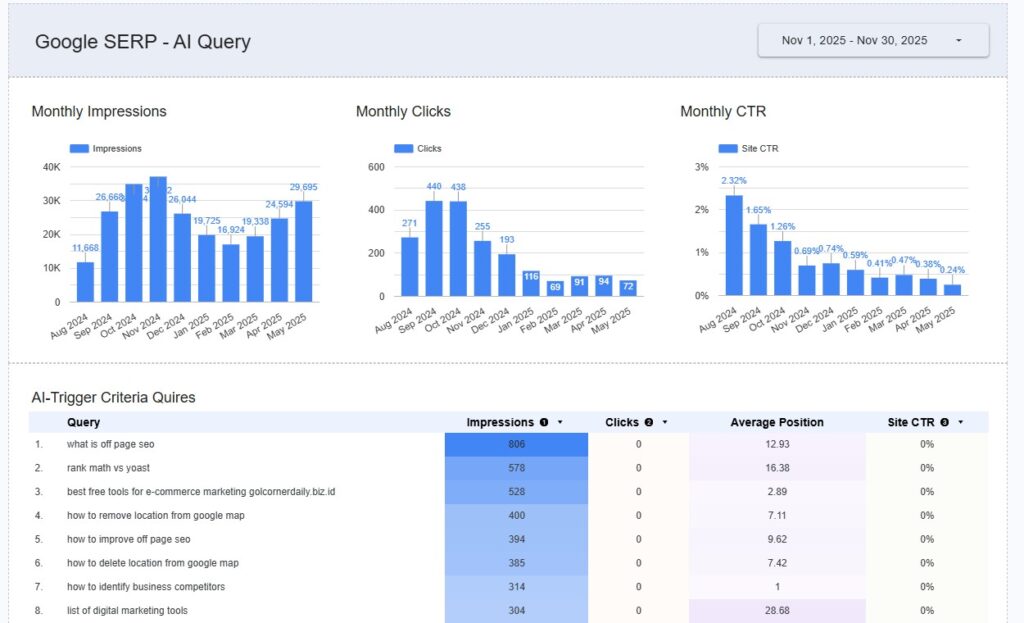
What you’re seeing: These are the specific URLs on your site that likely rank for these AI-triggering queries. Think of these as landing pages and citation sources for AI-prompts in Google SERPs.
The Insight: If you see a page with massive Impressions under this filter but a very low CTR (Click-Through Rate), an AI Overview is probably answering the user’s question before they need to click your link. These are your most vulnerable pages for AI impact, even if SEO rankings remain high.
Country-Level Rollout Tracking
Keep the filter on and click the Countries tab.
What you’re seeing: Where these conversational queries are coming from geographically. If you are a multinational, multilingual brand operating across several countries, you should be able to prompt any LLM for a new Regex Filter tailored to the specific language you need, based on feeding it this version.
The Insight: Google rolls out AI features in different regions at different times. By monitoring CTR on this filter by country, you can actually spot when AI Overviews become dominant in a new region—you will likely see impressions stay stable while clicks drop sharply in that specific country.
For The Marketing Pros: The “Now or Never” Benchmark
Using this filter in GSC is great, but taking it to a reporting dashboard (like Looker Studio) is how you save your strategy for 2026.
If you are struggling to explain traffic drops to your C-Suite or clients, it is “now or never” time.
Google Search Console’s API only retains 16 months of data. As we move deeper into 2025, the “Pre-AI” data from late 2023 and early 2024 is falling off that rolling window. Once that data is gone, you lose the ability to prove that your traffic drop was caused by a platform shift (AI Overviews) rather than a performance failure.
How to Calculate Your “AI Tax”

Don’t just report the drop; contextualize it. Use this filter to set a new baseline for 2026:
Isolate the Segment: Apply the Regex filter in GSC.
Compare the Eras: Compare the CTR of this segment from the start of your 16-month data (Pre-AI saturation) vs. the last 3 months.
Define the Tax: If your CTR dropped from 12% to 6%, you have a 50% “AI Tax” on informational queries.
The real insight is that everyone is different. Some sites are more news-focused, others are more B2C. You can’t compare these! However, this query filter will help you determine how much AI Overviews is siphoning off your specific content and SEO clicks.
Ahrefs did a study showing a ~34% drop. Search Engine Land does a good job showing a 61% drop in organic CTR in 2025.
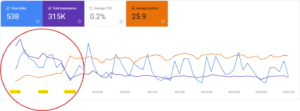
Here is an example showing how search Impressions (AI Overviews) are up month-to-month but SERP clicks started to die in November 2024 and are not coming back. The hidden value is “AI Brand Visibility” which is not nothing – it’s just hard to quantify. I put AI brand rankings above billboards on the highway and radio ads – so all is not lost. It’s just a recalibration of how we communicate and report on things.
Hopefully, the AI-overview siphon of your content is a net positive despite the click drop. As mentioned, every website is unique and has (or hasn’t) focused on this type of content for its marketing/SEO gains in the past.
If you need help determining how much AI has impacted your organic search traffic, please reach out to us. We can perform a custom calculation based on your unique data and help you set realistic expectations for 2026.